
The European financial and insurance sectors are raspberry robin This is because the worm continues to evolve its post-exploitation capabilities while remaining under the radar.
“What is unique about this malware is that it is highly obfuscated and very complex to statically disassemble,” Security Joes said in a new report published Monday. .
The observed intrusions against Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking organizations are notable for collecting more victim machine data than previously documented, and the malware is now highly resistant to analysis. technology.
Raspberry Robin (also known as the QNAP worm) has been used by multiple attackers as a means to gain a foothold into targeted networks. This framework spreads via infected USB drives and other methods and has recently been used in attacks targeting telecommunications and government sectors.

Microsoft is tracking the Raspberry Robin operator under the name DEV-0856.
Security Joes’ forensic investigation into one such attack revealed the use of 7-Zip files. This file is downloaded from the victim’s browser via social engineering and contains an MSI installer file designed to drop multiple modules.
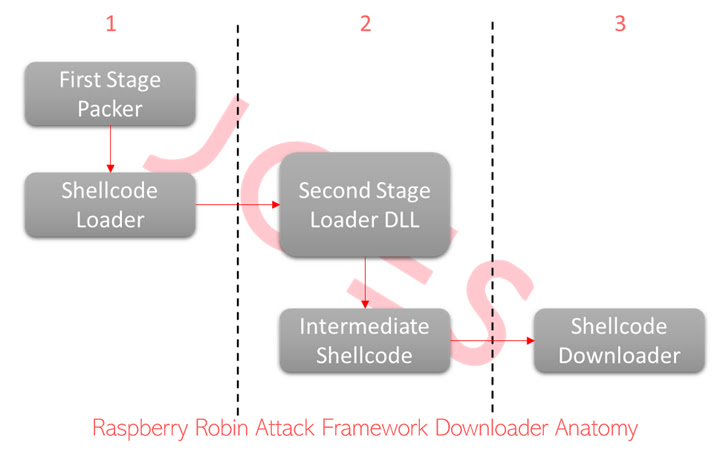
In another instance, a victim allegedly downloaded a ZIP file via a deceptive advertisement hosted on a domain known to distribute adware.
Archive files stored on Discord servers contain encoded JavaScript code that, when executed, drops a downloader protected by multiple layers of obfuscation and encryption to avoid detection.
While shellcode downloaders are primarily designed to retrieve additional executables, we’ve also seen significant upgrades to profile victims so they can deliver appropriate payloads, and in some cases , may even resort to a kind of ploy of offering bogus malware.
This includes the host’s Universally Unique Identifier (UUID), processor name, attached display device, and time (in minutes) since system boot, as well as hostname and username information collected by older versions of the malware. It is included.
Reconnaissance data is encrypted using a hardcoded key and sent to a command and control (C2) server. The C2 server responds with a Windows binary, running on your machine.
“Not only did we find a version of the malware that was several times more complex, but we also discovered that C2 beacons that used URLs containing plaintext usernames and hostnames now have payloads encrypted with robust RC4. We also found it,” said researcher Felipe Duarte.











